剑指offer24:反转链表
题目:输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头.
思路一:链表反转,需将节点指向改变. 可以每次取下一个节点向之前的节点中插入,采用头插法实现.需要三个指针,分别指向反转链表的头节点,旧链表中下一个代插入节点,以及此节点的下一个节点的指针(防止断链).
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead==nullptr)
return nullptr;
ListNode* newHead =pHead;
ListNode* p1 = pHead->next;
ListNode* p2 = nullptr;
newHead->next = nullptr;
while(p1!=nullptr){
p2 = p1->next;
p1->next = newHead;
newHead = p1;
p1 = p2;
}
return newHead;
}
思路二:上诉采用头插法,后面的节点变为前面的,有种栈的感觉,因此可以使用栈实现,但复杂度变大,作开拓思路用.
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead==nullptr)
return nullptr;
stack<ListNode*> st;
ListNode* newHead =nullptr;
ListNode* p1 = pHead;
ListNode* p2 = newHead;
while(p1!=nullptr){
st.push(p1);
p1 = p1->next;
}
while(!st.empty()){
ListNode* tmp = st.top();
tmp->next= nullptr; //断链
st.pop();
if(newHead==nullptr){
newHead=tmp;
p2 =newHead;
}
else{
p2->next=tmp;
p2=p2->next;
}
}
return newHead;
}
当使用栈可以实现时,就可以想到递归实现, 递归时需要将最后一个节点作为头节点返回. 对于其他节点的反转,是将其下一个节点指向的next指针指向它:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead==nullptr || pHead->next==nullptr)
return pHead;
ListNode* newHead = ReverseList(pHead->next);
pHead->next->next=pHead;
pHead->next=nullptr;
return newHead;
}
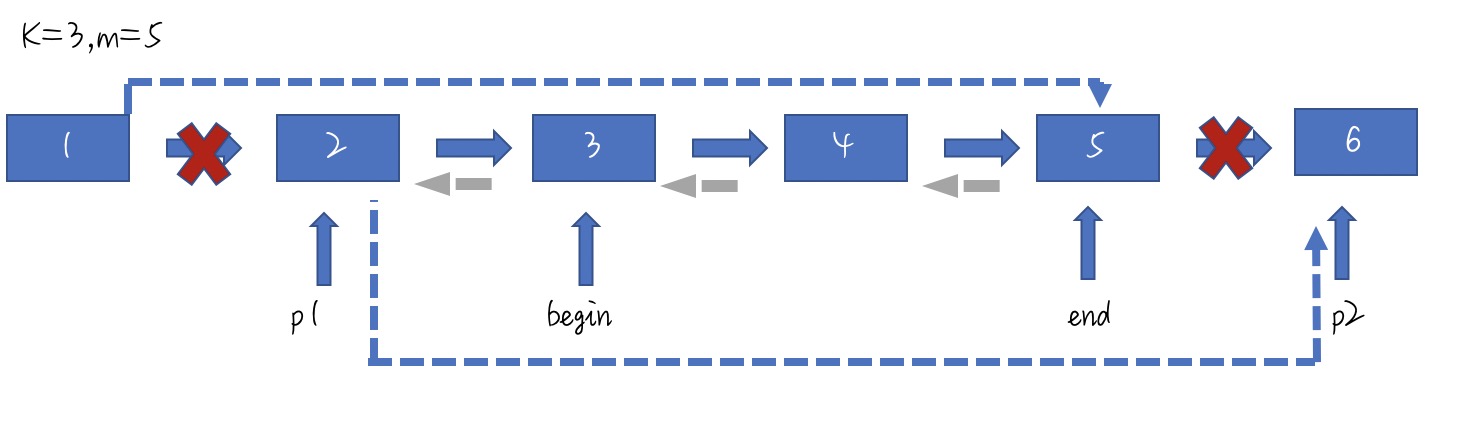
拓展:网易的一道面试题,给一个链表,指定反转从k至m的区间. 若k到m区间存在,对区间内的链表进行 反转后,需再将链表两端接上.
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead==nullptr)
return nullptr;
ListNode* newHead =pHead;
ListNode* p1 = pHead->next;
ListNode* p2 = nullptr;
newHead->next = nullptr;
while(p1!=nullptr){
p2 = p1->next;
p1->next = newHead;
newHead = p1;
p1 = p2;
}
return newHead;
}
ListNode* ReversePatialList(ListNode* pHead, int k, int m){
if(pHead==nullptr || k>=m)
return nullptr;
ListNode* p1=pHead;
ListNode* p2=nullptr;
ListNode* begin=nullptr;
ListNode* end=pHead;
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
if(i<k){
if(i != k-1){
p1 = p1->next;
if(p1==nullptr)
return nullptr;
}
else{
begin= p1->next;
}
}
end = end->next;
if(end==nullptr)
return nullptr;
}
p2 = end->next;
end->next=nullptr;
ReverseList(begin);
p1->next = end;
begin->next=p2;
return pHead;
}

